
What Do Nfs Mean – Let’s Talk About This!
Network File System (NFS) is a cornerstone of distributed computing, facilitating seamless file sharing across networks since its inception by Sun Microsystems in the 1980s.
Dive into the journey of Network File System (NFS), a file-sharing pioneer born with Sun Microsystems. From its origins to modern data management, explore how NFS continues to play a vital role in distributed networks.
This article explores Network File System (NFS), detailing its evolution and significance in streamlining file sharing and data management across diverse computing environment.
Table of Contents
ToggleA Comprehensive Exploration Of Network File System – Explore It Out!
Network File System (NFS) is a critical component in the realm of distributed computing, serving as a cornerstone for seamless data sharing and file access across networked environments.
Developed by Sun Microsystems in the 1980s, NFS has evolved into a widely adopted and standardized protocol, playing a pivotal role in simplifying data management across diverse computing systems.
This article delves into the intricacies of NFS, exploring its origins, core principles, key features, and the evolving landscape of networked file systems.
Origins and Evolution:
The genesis of NFS dates back to the collaborative efforts of Sun Microsystems, led by a team that included Sun’s co-founder Bill Joy. NFS was introduced in 1984 as an innovative solution to address the challenges of sharing files between computers in a networked environment.

The protocol’s design aimed to provide a simple and efficient mechanism for remote file access, allowing seamless communication between different operating systems.
Key Principles:
At its core, NFS operates on a client-server model, where a central server hosts the files and clients access these files over the network. The protocol relies on Remote Procedure Call (RPC) mechanisms for communication between the client and server.
NFS employs a stateless design, meaning that the server does not store information about the state of clients. This simplicity enhances scalability and reliability.
Read Also:MYSTIC MONK COFFEE SCANDAL – UNRAVELING A CONTROVERSY!
Streamlining File Access And Performance In Distributed Environments – Let’s Read!
Transparent Access:
At its core, NFS operates on a client-server model, where a central server hosts the files and clients access these files over the network. The protocol relies on Remote Procedure Call (RPC) mechanisms for communication between the client and server.
NFS employs a stateless design, meaning that the server does not store information about the state of clients. This simplicity enhances scalability and reliability.
Interoperability:
One of NFS’s strengths lies in its ability to operate across heterogeneous environments, supporting various operating systems. This interoperability has contributed to the protocol’s widespread adoption in diverse computing ecosystems.
Scalability:
NFS’s stateless design and decentralized approach contribute to its scalability. As the number of clients increases, NFS can efficiently handle the growing demand for file access, making it suitable for large-scale deployments.
Performance Optimization:
NFS continuously evolves to improve performance, with features like caching mechanisms, reduced latency, and support for parallel access. These optimizations aim to enhance the overall speed and responsiveness of file operations.
Challenges, Solutions, And Future Trends In File Sharing – Let’s Find Out!
Security Considerations:
While NFS simplifies file sharing, security considerations are paramount in networked environments.NFSv4, in particular, introduced robust security features, including support for Kerberos-based authentication and the ability to enforce access control policies.
These measures help mitigate potential security vulnerabilities and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data.
Challenges and Solutions:
Despite its strengths, NFS faces challenges, such as the potential for security vulnerabilities in earlier versions and the need for efficient handling of network disruptions.
However, ongoing developments in the protocol, coupled with the adoption of NFSv4, have addressed many of these concerns. Additionally, third-party solutions and best practices help enhance NFS deployment security and resilience.
The Future of NFS:
As technology advances, the role of NFS continues to evolve. Emerging trends, such as the widespread adoption of cloud computing and the increasing importance of edge computing, pose new challenges and opportunities for NFS.

Efforts to integrate NFS with modern storage solutions, like object storage, further extend the protocol’s relevance in contemporary computing landscapes.
Disadvantages Of Network File System – Here To Know!
Security:
First and foremost is a security concern, given that NFS is based on RPCs which are inherently insecure and should only be used on a trusted network behind a firewall. Otherwise, NFS will be vulnerable to internet threats.
Protocol chattiness:
First and foremost is a security concern, given that NFS is based on RPCs which are inherently insecure and should only be used on a trusted network behind a firewall. Otherwise, NFS will be vulnerable to internet threats.
Read Also:833 AREA CODE – UNLOCK THE MYSTERIES!
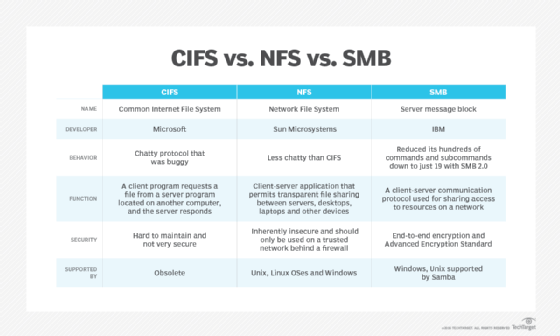
File sharing is highly complex:
Configuring and setting up proper shared file access via file locking and caching is a daunting task at best. On the one hand, it adds a lot of the protocol overhead, leading to the chattiness mentioned above.
On the other hand, it still leaves a lot to be desired, inasmuch any each host’s mount command for the same file system can easily go awry.
Parallel file access:
NFS was designed as a way to sequentially access a shared network file, but these days applications are dealing with larger files, and non-sequential or parallel file access is required. This was added to NFSv4, but not a lot of clients support it yet.
Block size limitations:
The current NFS protocol standard allows for a maximum of 1MB of data to be transferred during one read or write request. In 1984, 1MB was a lot of data, but that’s no longer the case. There are classes of applications that should be transferring GBs not MBs of data.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is NFS suitable for large-scale deployments?
Yes, NFS’s stateless design and scalability features make it well-suited for large-scale deployments, efficiently managing increased demands for file access as the number of clients grows.
2. What challenges does NFS face?
NFS faces challenges like potential security vulnerabilities in earlier versions and the need for efficient handling of network disruptions. However, ongoing developments and the adoption of NFSv4 have addressed many of these concerns.
3. How does NFS ensure security?
NFS faces challenges like potential security vulnerabilities in earlier versions and the need for efficient handling of network disruptions. However, ongoing developments and the adoption of NFSv4 have addressed many of these concerns.
4. Can NFS operate in heterogeneous environments?
NFS excels in operating across diverse systems, supporting multiple operating systems seamlessly. This interoperability has fueled its widespread adoption in diverse computing environments.
Conclusion:
NFS remains a stalwart in file sharing. Its cross-system compatibility and scalability cement its relevance. As technology advances, adapts, ensuring its pivotal role in the evolving tapestry of distributed computing.
- Read Also: SNOKIDO – YOUR ULTIMATE GAMING COMPANION!

Does Pooph Work - Try it today!
You May Also Like

Katianna Stoermer Coleman – Learn more about Katianna!
February 19, 2024
Anime Drawings – A Step-by-Step Guide!
March 1, 2024
